Description of the procedure
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure that repairs problems with the septum. The septum divides the two nostrils of the nose and is made of cartilage (a thick flexible material) and bone.
Doctors may perform this procedure in combination with other surgical procedures, including plastic surgery. It is performed either under general or local anesthesia in a hospital or clinic.
When should this procedure be performed?
Your doctor will recommend when and how frequently this procedure is required.
Septoplasty is usually not done within 6 months of a traumatic injury to the nose. Repeating the procedure may be necessary if it does not fully restore breathing or correct the problem, or if the problem returns.
Why is this procedure performed?
Septoplasty helps restore normal breathing for people who suffer from blockage of the nasal airways. Blockage may contribute to sleep apnea, a potentially dangerous condition where a person stops breathing for a period of time while sleeping.
Other reasons to perform septoplasty include:
- controlling headaches caused by pressure on the septum
- controlling persistent nosebleeds
- removing or repairing a structural problem of the septum (e.g., an abnormal shape)
- relieving persistent sinus infections
Are there any risks and precautions?
Certain risks are common to all surgery and anesthesia. These risks depend on many factors including the type of surgery and your own medical condition. The possible, but very rare, side effects include side effects of the anesthetic, breathing problems, infection, bleeding, scarring, and death.
Although septoplasty is generally considered safe, it does have some risk of side effects or complications. These include:
- alterations in your nose shape
- bleeding
- damage to the septum (septal perforation)
- decreased sense of smell
- infection
- numbness in the nose tip or upper front teeth
- pooling of blood around the surgical site (septal hematoma)
- scarring
There is also a chance that your nasal symptoms might continue even after the surgery.
If you are concerned about any symptoms following this procedure, speak to your doctor.
Take the time to be sure you understand all the risks of complications and side effects as well as any precautions you or your doctor can take to avoid them. Be sure your doctor understands all your concerns.
What happens during the procedure?
You will be given either general or local anesthesia before the procedure begins.
- The surgeon makes an incision inside the nasal passage on one side of the septum.
- The surgeon then removes material that is blocking the nasal passage, straightens the area, or performs any other necessary surgery.
- The tissue over the septum is stitched back in place and the entire nose is tightly packed with bandages and gauze to prevent bleeding.
If extensive cutting is done, splints may be required to provide additional support to the cartilage of the nose. The surgery may take 1 to 1.5 hours.
How should I prepare for this procedure?
Before having this procedure, discuss the advantages, disadvantages, long-term risks, and consequences associated with the procedure with your doctor. Be sure you fully understand what will happen and are comfortable with your doctor's answers to your questions.
Before the procedure, your doctor will check your general health as well as your nasal passage to see how air flows in the nostrils.
If a general anesthetic will be used, do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before the procedure. If your doctor has recommended different times, follow the timing recommended by your doctor.
Tell your doctor about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), dietary supplements, and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the procedure.
Arrange for someone to drive you home from the hospital because you may still feel groggy from the anesthesia.
What can I expect after the procedure?
Most people go home the same day as their surgery. Doctors often recommend using ice to control pain and swelling. Pain-relieving medications may also be prescribed to help reduce pain. There may also be some bruising, numbness, bleeding, and discoloration. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully to prevent damage to the septum as it heals.
Keep your nose dry and avoid touching, rubbing, or blowing your nose. All packing within the nose will be removed before you go home or up to 1.5 days after surgery. You should rest and sleep with your head elevated to help reduce swelling. Follow the specific care instructions provided by your doctor.
You should avoid strenuous activity for 2 to 4 weeks. Most people are able to return to work or school 1 week after the procedure.
Call your doctor if you experience:
- heavy bleeding from the nose
- pain that gets worse over time
- difficulty breathing
- fever
Results
Results vary depending on the reason that the septoplasty was done. The procedure is often effective for correcting structural problems, controlling persistent nosebleeds, unblocking the nasal airways, and controlling headaches caused by pressure on the septum.
Healing requires time and it may take up to a year before you notice the complete results.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Septoplasty
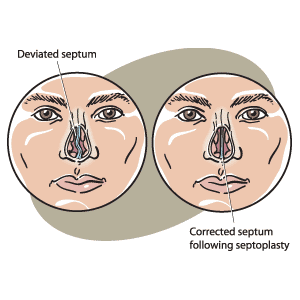
A deviated septum (left) can be corrected with a septoplasty procedure (right).